BUSINESS STATISTICS: CONSTRUCTION OF INDEX NUMBER AND FORMULAS
INDEX NUMBER
Introduction:
Index number is an indicator of changes in prices and quantities. It is a specialized average designed to measure the change in a group of related variables over a period of time.
It is also an indicator of inflationary or deflationary tendencies.
Features of Index Number:
Following are the various feature of index number:
1. Measures of relative changes: Index number measure relative or percentage changes in the variable over time.
2. Quantitative expression: Index numbers offer a precise measurement of the quantitative change in the concerned variable over time.
3. Average: Index number show changes in terms of
average.
Advantages of Index Number:
1. Measurement of change in the
price level or the value of money: Index number can be used to know the impact of the change
in the value of money on different sections of the society.
2. Knowledge of the change in
standard of living: Index number helps to ascertain the living standards of
people. Money income may increase but if index number show a decrease in the
value if money. Living standard may even decline.
3. Adjustment in salaries and
allowances: Cost
of living index number is a useful guide to the government and private
enterprises to make necessary adjustment in salaries and allowances of the
workers.
4. Useful to business
community: Price index
numbers serve as a useful guide to the business community in planning.
5. Information regarding
foreign trade: Index of exports and imports provides useful information
regarding foreign trade.
Limitation of Index Number:
1. Not completely true: Index number not fully true. The index
number simply indicate arithmetical tendency of the temporal changes in the
variable.
2. International comparison is
not possible: Different
countries have different bass of index numbers; these do not help international
comparisons.
3. Difference of time: With the passage of time, it is
difficult to make comparison of index number. With the changing time man’s
habits.
4. Limited use: Index numbers are prepared with certain
specific objective. If they are used for another purpose they may lead to wrong
conclusion.
5. Lack of retail price index
number: Most of the
index numbers are prepared on the basis of wholesaler prices. But in real life,
retail prices are most relevant, but it is difficult to collect retail prices.
Main Problems in the
construction of Index Number:
1. Purpose of index number: There are various types of index number,
constructed with different objectives. Before constructing an index number, one
must define the objective.
2. Selection of base year: Selection of base year is another
problem in the construction of index number. Base year is the reference year.
It is the year with which prices of the current year are compared.
3. Selection of goods and
services: Having
defined the objective, the problem is of the selection of goods or services to
be included in the index number.
4. Selection of price: whether wholesale or retail prices are
used is also a problem in construction of index number.
5. Other problems:
i. Choice of average (simple or geometric
average)
ii. Selection of appropriate weights
iii. Selection of appropriate formula
(Fisher’s or laspeyre's)
DIFFERENT FORMULA FOR INDEX NUMBERS:
- LASPEYER′ S INDEX NUMBER = (∑p1q0)/(∑p0q0) X 100
- PAASCHE′ S INDEX NUMBER = (∑p1q1)/(∑p0q1) X 100
- MARSHAL &EDGEWORTH′ S INDEX NUMBER = (∑p1q0) +(∑p1q1) / (∑p0q0) + (∑p0q1) X 100
- DORBISH & BOWLEY'S INDEX NUMBER = LASPEYER + PAASCHE / 2
- FISHER'S INDEX NUMBER = √(L X P)
- FISHER'S TIME REVERSAL TEST =
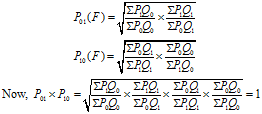
- FISHER'S FACTOR REVERSAL TEST =
√{(∑p1q0)/(∑p0q0) X
(∑p1q1)/(∑p0q1) X
(∑p 0q1)/(∑p0q0) X
(∑p1q1)/(∑p1q0)} = (∑p1q1)/(∑p0q0)
FOR BETTER UNDERSTANDING WATCH THIS VIDEO:
REPLY US ON :
spardasmartacademy@gmail.com
Comments
Post a Comment